使用OpenSSL,创建本地调试HTTPS证书
在本地开发环境中,为了模拟线上完整环境,需要配置https证书。网上的资料太老了,现在都马上2024年了,我觉得有必要出一个比较新,比较简单的证书制作教程。其实除了本地可以用,只要用户导入了,都能算是信任证书。
制作分4步走,最重要的一步就是准备配置文件的时候。

下载openssl
windows下载安装包:https://slproweb.com/products/Win32OpenSSL.html
安装完成后,使用CMD进入程序的bin目录。如果你安装在D盘,大概就是D:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64\bin
生成CA根证书
执行cmd命令,创建key文件
openssl genrsa -out myCA.key 2048通过key加密机构信息形成公钥,有效期一百年
openssl req -new -x509 -key myCA.key -out myCA.cer -days 36500运行后,会让你填写内容,内容随便乱写就是了。
| 参数名称 | 参数值 |
|---|---|
| Country Name | 国家代码,比如中国就是CN |
| State or Province Name | 省名称 |
| Locality Name | 城市名称 |
| Organization Name | 机构名称 |
| Organizational Unit Name | 机构单位名称 |
| Common Name | 授权给谁 |
| Email Address | 邮件地址 |
创建服务器证书
openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048创建配置文件,在bin目录下载创建一个名为:openssl.cnf的文件
文件内容见下面。
其中[ alt_names ]项里面的
DNS.1 = *.example.com
DNS.2 = example.com
可以改成你的域名,多个域名DNS.3、DNS.4这样走。通配符是*.mytest.com,这样,所有mytest.com子域名都能用。
#
# OpenSSL example configuration file.
# See doc/man5/config.pod for more info.
#
# This is mostly being used for generation of certificate requests,
# but may be used for auto loading of providers
# Note that you can include other files from the main configuration
# file using the .include directive.
#.include filename
# This definition stops the following lines choking if HOME isn't
# defined.
HOME = .
# Use this in order to automatically load providers.
openssl_conf = openssl_init
# Comment out the next line to ignore configuration errors
config_diagnostics = 1
# Extra OBJECT IDENTIFIER info:
# oid_file = $ENV::HOME/.oid
oid_section = new_oids
# To use this configuration file with the "-extfile" option of the
# "openssl x509" utility, name here the section containing the
# X.509v3 extensions to use:
# extensions =
# (Alternatively, use a configuration file that has only
# X.509v3 extensions in its main [= default] section.)
[ new_oids ]
# We can add new OIDs in here for use by 'ca', 'req' and 'ts'.
# Add a simple OID like this:
# testoid1=1.2.3.4
# Or use config file substitution like this:
# testoid2=${testoid1}.5.6
# Policies used by the TSA examples.
tsa_policy1 = 1.2.3.4.1
tsa_policy2 = 1.2.3.4.5.6
tsa_policy3 = 1.2.3.4.5.7
# For FIPS
# Optionally include a file that is generated by the OpenSSL fipsinstall
# application. This file contains configuration data required by the OpenSSL
# fips provider. It contains a named section e.g. [fips_sect] which is
# referenced from the [provider_sect] below.
# Refer to the OpenSSL security policy for more information.
# .include fipsmodule.cnf
[openssl_init]
providers = provider_sect
# List of providers to load
[provider_sect]
default = default_sect
# The fips section name should match the section name inside the
# included fipsmodule.cnf.
# fips = fips_sect
# If no providers are activated explicitly, the default one is activated implicitly.
# See man 7 OSSL_PROVIDER-default for more details.
#
# If you add a section explicitly activating any other provider(s), you most
# probably need to explicitly activate the default provider, otherwise it
# becomes unavailable in openssl. As a consequence applications depending on
# OpenSSL may not work correctly which could lead to significant system
# problems including inability to remotely access the system.
[default_sect]
# activate = 1
####################################################################
[ ca ]
default_ca = CA_default # The default ca section
####################################################################
[ CA_default ]
dir = ./demoCA # Where everything is kept
certs = $dir/certs # Where the issued certs are kept
crl_dir = $dir/crl # Where the issued crl are kept
database = $dir/index.txt # database index file.
#unique_subject = no # Set to 'no' to allow creation of
# several certs with same subject.
new_certs_dir = $dir/newcerts # default place for new certs.
certificate = $dir/cacert.pem # The CA certificate
serial = $dir/serial # The current serial number
crlnumber = $dir/crlnumber # the current crl number
# must be commented out to leave a V1 CRL
crl = $dir/crl.pem # The current CRL
private_key = $dir/private/cakey.pem # The private key
x509_extensions = usr_cert # The extensions to add to the cert
# Comment out the following two lines for the "traditional"
# (and highly broken) format.
name_opt = ca_default # Subject Name options
cert_opt = ca_default # Certificate field options
# Extension copying option: use with caution.
# copy_extensions = copy
# Extensions to add to a CRL. Note: Netscape communicator chokes on V2 CRLs
# so this is commented out by default to leave a V1 CRL.
# crlnumber must also be commented out to leave a V1 CRL.
# crl_extensions = crl_ext
default_days = 365 # how long to certify for
default_crl_days= 30 # how long before next CRL
default_md = default # use public key default MD
preserve = no # keep passed DN ordering
# A few difference way of specifying how similar the request should look
# For type CA, the listed attributes must be the same, and the optional
# and supplied fields are just that :-)
policy = policy_match
# For the CA policy
[ policy_match ]
countryName = match
stateOrProvinceName = match
organizationName = match
organizationalUnitName = optional
commonName = supplied
emailAddress = optional
# For the 'anything' policy
# At this point in time, you must list all acceptable 'object'
# types.
[ policy_anything ]
countryName = optional
stateOrProvinceName = optional
localityName = optional
organizationName = optional
organizationalUnitName = optional
commonName = supplied
emailAddress = optional
####################################################################
[ req ]
default_bits = 2048
default_keyfile = privkey.pem
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
attributes = req_attributes
x509_extensions = v3_ca # The extensions to add to the self signed cert
# Passwords for private keys if not present they will be prompted for
# input_password = secret
# output_password = secret
# This sets a mask for permitted string types. There are several options.
# default: PrintableString, T61String, BMPString.
# pkix : PrintableString, BMPString (PKIX recommendation before 2004)
# utf8only: only UTF8Strings (PKIX recommendation after 2004).
# nombstr : PrintableString, T61String (no BMPStrings or UTF8Strings).
# MASK:XXXX a literal mask value.
# WARNING: ancient versions of Netscape crash on BMPStrings or UTF8Strings.
string_mask = utf8only
# req_extensions = v3_req # The extensions to add to a certificate request
[ req_distinguished_name ]
countryName = Country Name (2 letter code)
countryName_default = AU
countryName_min = 2
countryName_max = 2
stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name)
stateOrProvinceName_default = Some-State
localityName = Locality Name (eg, city)
0.organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company)
0.organizationName_default = Internet Widgits Pty Ltd
# we can do this but it is not needed normally :-)
#1.organizationName = Second Organization Name (eg, company)
#1.organizationName_default = World Wide Web Pty Ltd
organizationalUnitName = Organizational Unit Name (eg, section)
#organizationalUnitName_default =
commonName = Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name)
commonName_max = 64
emailAddress = Email Address
emailAddress_max = 64
# SET-ex3 = SET extension number 3
[ req_attributes ]
challengePassword = A challenge password
challengePassword_min = 4
challengePassword_max = 20
unstructuredName = An optional company name
[ usr_cert ]
# These extensions are added when 'ca' signs a request.
# This goes against PKIX guidelines but some CAs do it and some software
# requires this to avoid interpreting an end user certificate as a CA.
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
# This is typical in keyUsage for a client certificate.
# keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
# PKIX recommendations harmless if included in all certificates.
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
# This stuff is for subjectAltName and issuerAltname.
# Import the email address.
# subjectAltName=email:copy
# An alternative to produce certificates that aren't
# deprecated according to PKIX.
# subjectAltName=email:move
# Copy subject details
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
# This is required for TSA certificates.
# extendedKeyUsage = critical,timeStamping
[ v3_req ]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
# Extensions to add to a certificate request
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
[ alt_names ]
DNS.1 = *.mytest.com
DNS.2 = *.test.com
[ v3_ca ]
# Extensions for a typical CA
# PKIX recommendation.
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid:always,issuer
basicConstraints = critical,CA:true
# Key usage: this is typical for a CA certificate. However since it will
# prevent it being used as an test self-signed certificate it is best
# left out by default.
# keyUsage = cRLSign, keyCertSign
# Include email address in subject alt name: another PKIX recommendation
# subjectAltName=email:copy
# Copy issuer details
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
# DER hex encoding of an extension: beware experts only!
# obj=DER:02:03
# Where 'obj' is a standard or added object
# You can even override a supported extension:
# basicConstraints= critical, DER:30:03:01:01:FF
[ crl_ext ]
# CRL extensions.
# Only issuerAltName and authorityKeyIdentifier make any sense in a CRL.
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid:always
[ proxy_cert_ext ]
# These extensions should be added when creating a proxy certificate
# This goes against PKIX guidelines but some CAs do it and some software
# requires this to avoid interpreting an end user certificate as a CA.
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
# This is typical in keyUsage for a client certificate.
# keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
# PKIX recommendations harmless if included in all certificates.
subjectKeyIdentifier=hash
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer
# This stuff is for subjectAltName and issuerAltname.
# Import the email address.
# subjectAltName=email:copy
# An alternative to produce certificates that aren't
# deprecated according to PKIX.
# subjectAltName=email:move
# Copy subject details
# issuerAltName=issuer:copy
# This really needs to be in place for it to be a proxy certificate.
proxyCertInfo=critical,language:id-ppl-anyLanguage,pathlen:3,policy:foo
####################################################################
[ tsa ]
default_tsa = tsa_config1 # the default TSA section
[ tsa_config1 ]
# These are used by the TSA reply generation only.
dir = ./demoCA # TSA root directory
serial = $dir/tsaserial # The current serial number (mandatory)
crypto_device = builtin # OpenSSL engine to use for signing
signer_cert = $dir/tsacert.pem # The TSA signing certificate
# (optional)
certs = $dir/cacert.pem # Certificate chain to include in reply
# (optional)
signer_key = $dir/private/tsakey.pem # The TSA private key (optional)
signer_digest = sha256 # Signing digest to use. (Optional)
default_policy = tsa_policy1 # Policy if request did not specify it
# (optional)
other_policies = tsa_policy2, tsa_policy3 # acceptable policies (optional)
digests = sha1, sha256, sha384, sha512 # Acceptable message digests (mandatory)
accuracy = secs:1, millisecs:500, microsecs:100 # (optional)
clock_precision_digits = 0 # number of digits after dot. (optional)
ordering = yes # Is ordering defined for timestamps?
# (optional, default: no)
tsa_name = yes # Must the TSA name be included in the reply?
# (optional, default: no)
ess_cert_id_chain = no # Must the ESS cert id chain be included?
# (optional, default: no)
ess_cert_id_alg = sha256 # algorithm to compute certificate
# identifier (optional, default: sha256)
[insta] # CMP using Insta Demo CA
# Message transfer
server = pki.certificate.fi:8700
# proxy = # set this as far as needed, e.g., http://192.168.1.1:8080
# tls_use = 0
path = pkix/
# Server authentication
recipient = "/C=FI/O=Insta Demo/CN=Insta Demo CA" # or set srvcert or issuer
ignore_keyusage = 1 # potentially needed quirk
unprotected_errors = 1 # potentially needed quirk
extracertsout = insta.extracerts.pem
# Client authentication
ref = 3078 # user identification
secret = pass:insta # can be used for both client and server side
# Generic message options
cmd = ir # default operation, can be overridden on cmd line with, e.g., kur
# Certificate enrollment
subject = "/CN=openssl-cmp-test"
newkey = insta.priv.pem
out_trusted = apps/insta.ca.crt # does not include keyUsage digitalSignature
certout = insta.cert.pem
[pbm] # Password-based protection for Insta CA
# Server and client authentication
ref = $insta::ref # 3078
secret = $insta::secret # pass:insta
[signature] # Signature-based protection for Insta CA
# Server authentication
trusted = $insta::out_trusted # apps/insta.ca.crt
# Client authentication
secret = # disable PBM
key = $insta::newkey # insta.priv.pem
cert = $insta::certout # insta.cert.pem
[ir]
cmd = ir
[cr]
cmd = cr
[kur]
# Certificate update
cmd = kur
oldcert = $insta::certout # insta.cert.pem
[rr]
# Certificate revocation
cmd = rr
oldcert = $insta::certout # insta.cert.pem然后保存文件以后,执行命令
openssl req -config openssl.cnf -new -out server.req -key server.key 再用这个key走一遍。然后会让你填写内容,跟上面一样。
openssl x509 -req -extfile openssl.cnf -extensions v3_req -in server.req -out server.cer -CAkey myCA.key -CA myCA.cer -days 36500 -CAcreateserial -CAserial serial信任证书
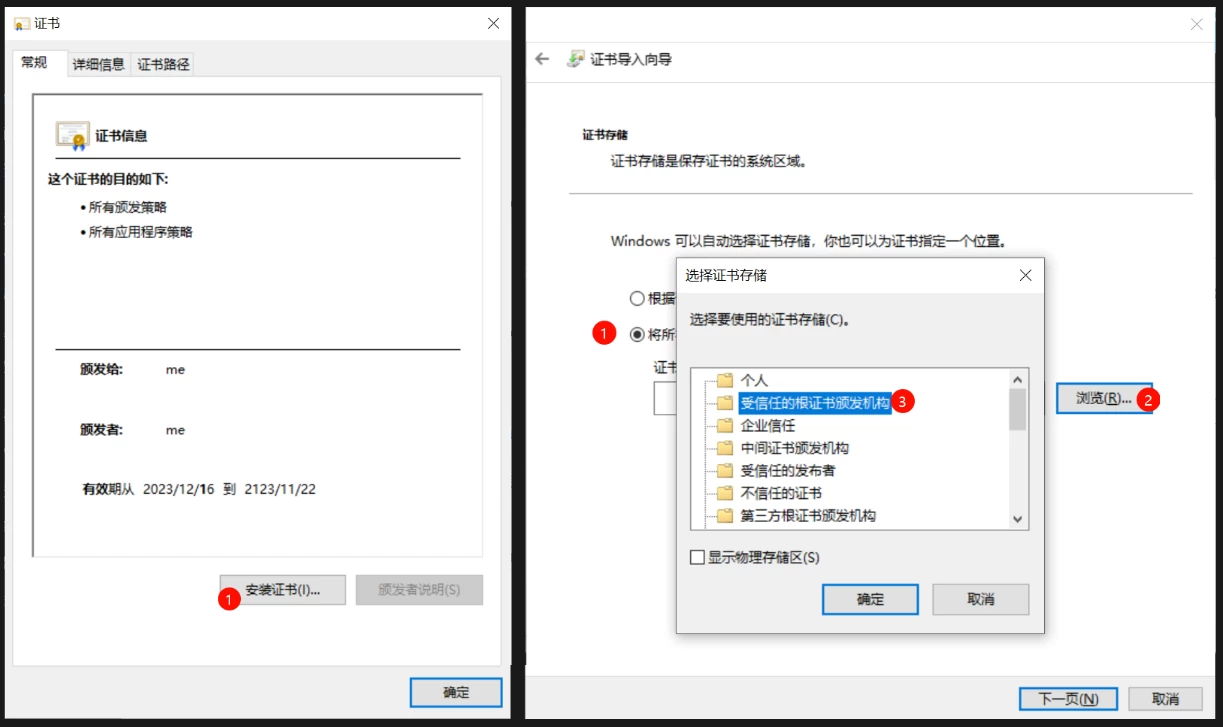
双击myCA.cer文件,进行点击安装证书。
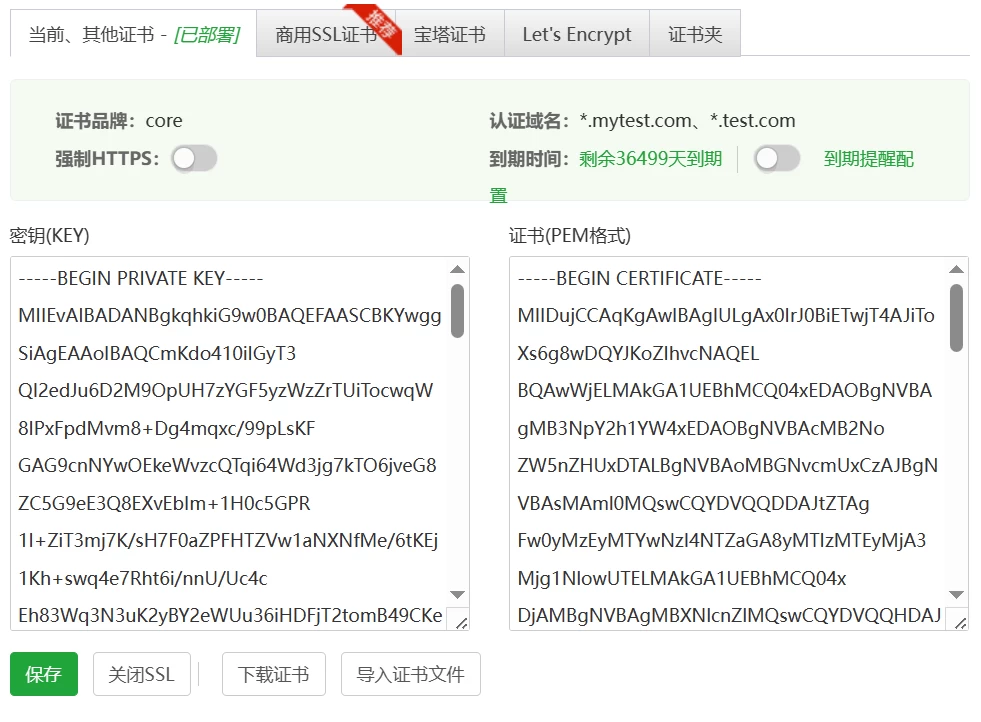
信任后。server.cer是pem文件,server.key是密钥。本地宝塔可以导入查看
浏览器里面也不会提示不安全了。
最重要的是配置文件。否则直接生成文件再组装,是没有用的。
阅读剩余
===================The End===================
版权声明:
作者:AC
链接:https://blog.hiac.me/archives/187
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载
版权声明:
作者:AC
链接:https://blog.hiac.me/archives/187
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载
THE END